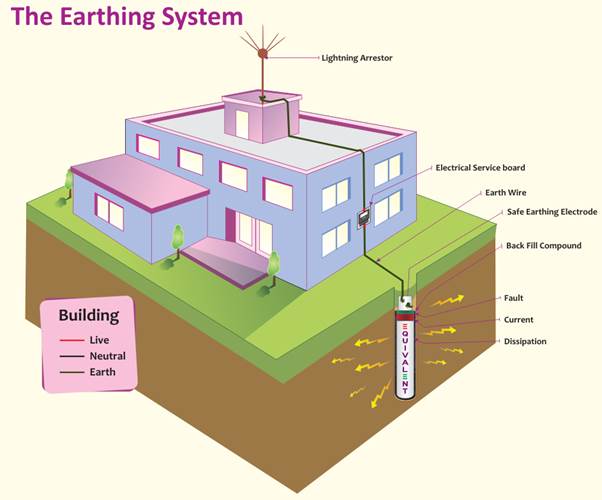
In Railway Signalling System Earthing play a vital Roles to Protect the Electronic equipment such as Electronics Interlocking System, IPS System, VDU panel, Monitoring Panel, Datalogger etc. In Railway Earthing Protection System based on the working and Protection capability the are divided into some Category.
Table of Contents
- What is Earthing:
- Advantages of Earthing:
- Types of Earthing Surge Protection System In Railway Signalling System:
What is Earthing:
Earthing is defined as “the process in which the instantaneous discharge of the electrical energy takes place by transferring charges directly to the earth through low resistance wire.”
Advantages of Earthing:
- Earthing is the safe and the best method of offering safety. We know that the earth’s potential is zero and is treated as Neutral. Since low equipment is connected to earth using low resistance wire, balancing is achieved.
- Metal can be used in electrical installations without looking for its conductivity, proper earthing ensures that metal does not transfer current.
- A sudden surge in voltage or overload does not harm the device and person if proper earthing measures are done.
- It prevents the risk of fire hazards that could otherwise be caused by the current leakage.
Types of Earthing Surge Protection System In Railway Signalling System:
- Class A Earthing Surge Protection
- Class B Earthing Surge Protection
- Class C Earthing Surge Protection
- Class D Earthing Surge Protection
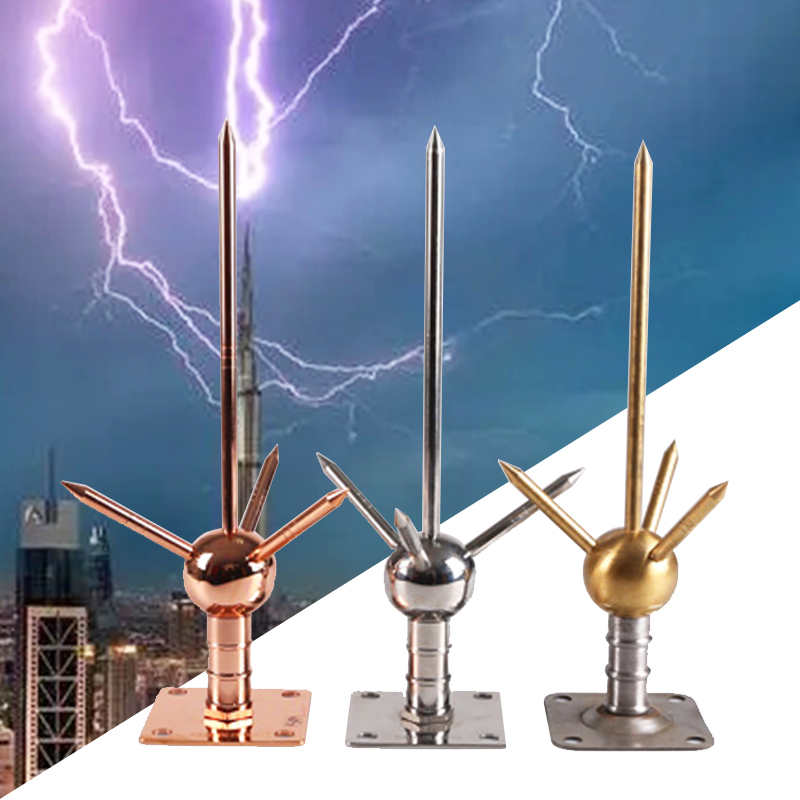
Class A Earthing Surge Protection:
Class A earthing usually uses either vertical or horizontal earth electrodes, or some times combination of both. This could means connecting the down conductors to a coper bounded earth rod that is buried in the ground . For Type A earthing the length of the vertical and horizontal earth electrodes to be connected to be each down conductor will be defined in the standard.
Example:

Class B Earthing Surge Protection
Class B Earthing protection basically Ring Earthing forms a perimeter around the structure.
For a standard Class B earth must have to follow the following conditions-
- be a closed ring of conductors If it is not possible to close the ring, a connection must be made inside the building using conductive metallic equipment such as pipes.
- be at least 0.5m below the surface
- be maintained at least 1 metre from the structure.
- have 80% of the length of the ring in contact with natural soil. Thus, no more than 20% of the total length may be in the basement of the structure instead of in direct contact with the soil.
- if the radius of the ring electrode is less than the length of vertical or horizontal earth electrodes required for Type A Earthing then additional horizontal or vertical earth electrodes can be connected to the ring.
Foundation Earth Electrodes are simply concrete reinforced foundations – they are considered to be Type B Earthing.
Example:

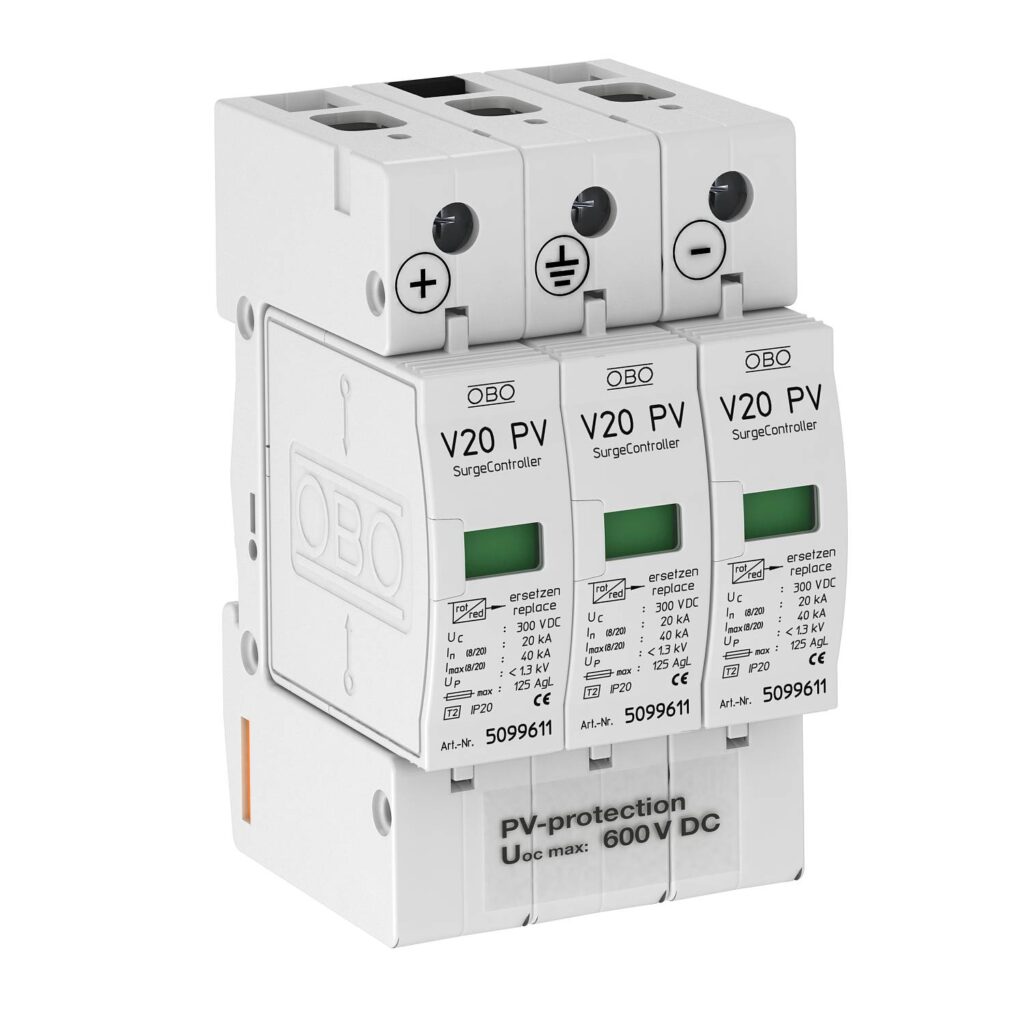
Class C Earthing Surge Protection
This type of Protection is provided against low voltage surges at the equipment input level connected between line and neutral.
The device is a single high capacity varistor (MOV) which have following additional features:
- Failure indication ( Defect indication) when device failed.
- Thermal disconnection of device when it starts having heavy leakage current due to ageing/ handling several surges.
- Potential free contact for remote monitoring.
Example:
Surge Protection Device (SPD), OBO

Class D Earthing Surge Protection
Class D type protection mainly protect the line to ground fault. It consist of numbers of fuses. Class D type protection we will install for small application. The main advantage of this type of protection is, if any short circuit happened in circuit then it will disconnect this particular circuit and isolate the hole system. Such as another circuit of this system will not effected. As a same words if any particular circuit we want to work something then no need to turn off full system. we can only disconnect this Circuit.
Example:
HRC fuse, Glass Fuse